OSI MODEL
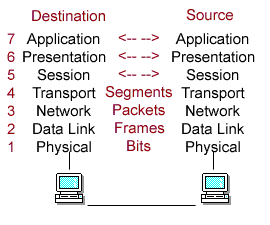
|
Physical |
This
layer conveys the bit stream through the network at the electrical and
mechanical level. It provides the hardware means of sending and receiving
data on a carrier. |
|
Data-Link |
Data
packets are encoded and decoded into electrical signals at this layer. It
furnishes transmission protocol knowledge and management. |
|
Network |
This
layer creates the logical paths, known as virtual circuits, for transmitting
data from node to node. Routing and Forwarding are functions of this
layer. |
|
Transport |
This
layer manages the end-to-end control (for example, determining whether all
packets have arrived) and error-checking. It ensures complete data transfer. |
|
Session |
This
layer sets up, coordinates, and terminates conversations, exchanges, and
dialogs between the applications at each end. It deals with session and
connection coordination. |
|
Presentation |
This
layer formats and encrypts data to be sent across a network. ). Sometimes
called the syntax layer. |
|
Application |
This is the layer at which communication partners
are identified, quality of service is identified, user authentication and
privacy are considered, and any constraints on data syntax are identified.
Application services are provided by this layer for file transfers, email,
and other network software services. |